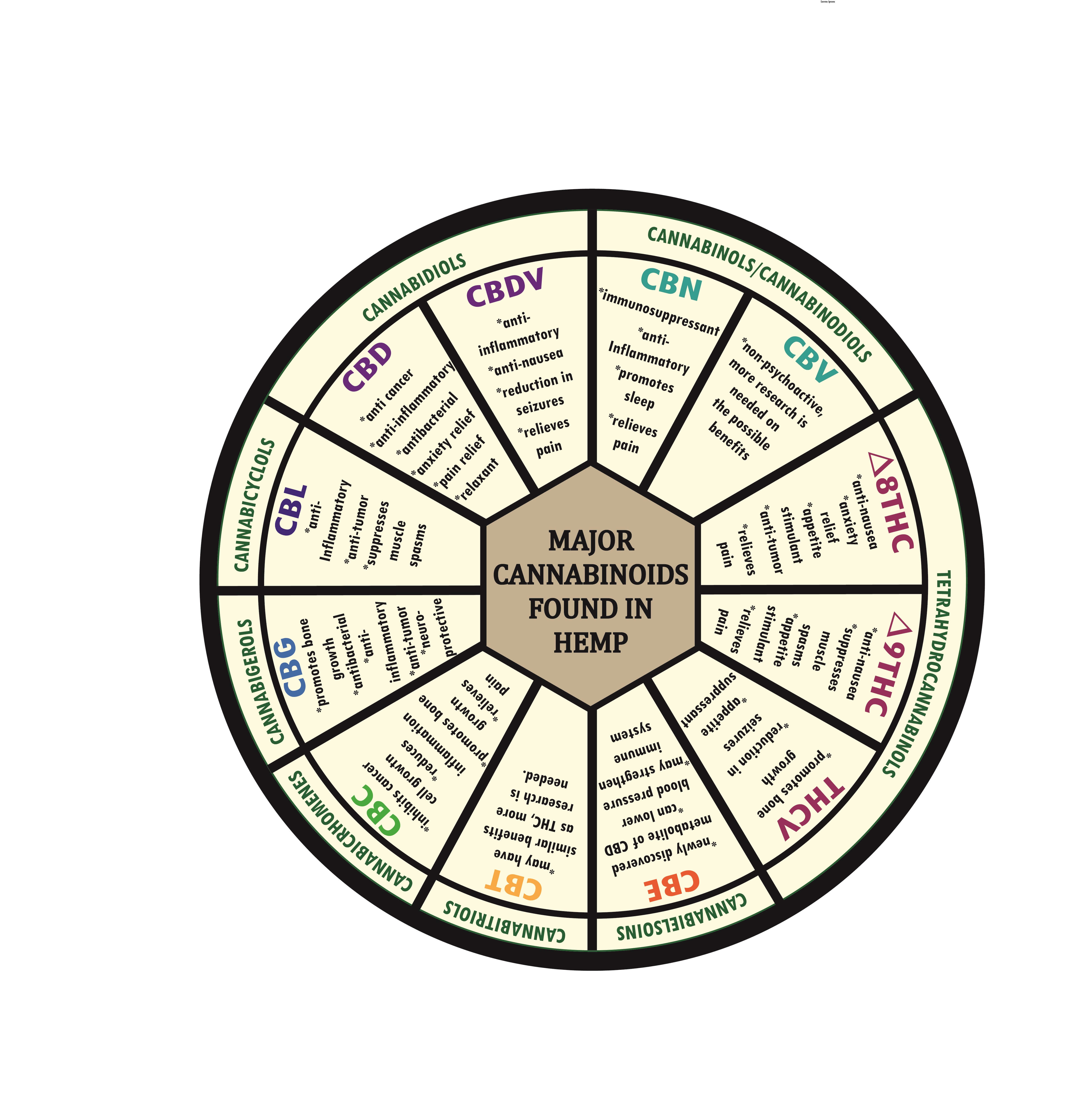
Full Spectrum Cannabinoids
including sleep, appetite, and mood.
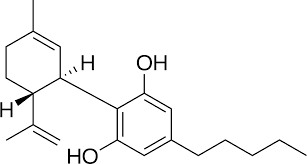
CBD
Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid abundant in many strains of hemp. It does not bind directly to CB1 and CB2 receptors, but reacts with and can increase production of the endocannabinoid 2-Arachidonolyglycerol (2-AG). 2-AG regulates several functions including sleep, memory, mood, appetite, and pain reception.
CBD is one of the most often studied cannabinoids. One of the well known benefits of CBD is its effect on seizures, decreasing both their occurrence rate and severity. The drug Epidiolex, which is used to treat seizures in Dravet Syndrome and Lennox-Gastaut Syndrome, is CBD-based. It has also shown potential as a neuroprotectant and may benefit Alzheimer’s patients. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects may potentially treat inflammatory auto immune disorders.
When paired with other cannabinoids and terpenes, CBD is thought to contribute to the “Entourage Effect”. This is the synergistic effect achieved when these cannabinoids and terpenes interact within the human body.

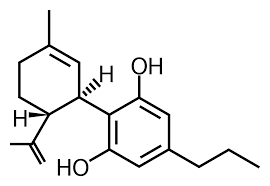
CBDV
Cannabidivarin (CBDV) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid found mainly in strains that are lower in THC. It is similar in structure to cannabidiol (CBD) and strains high in CBD also tend to have higher amounts of CBDV.
CBDV has been shown in studies to reduce nausea and inflammation. It can also lessen the severity and frequency of seizures.
In this 2013 study, CBDV, THC, and THCV were shown to reduce nausea in rats. GW Pharmaceuticals, the company that developed the drug Epidiolex, is now developing a GPW42006. This CBDV based drug is designed to reduce the frequency and severity of seizures.
Capsaicin receptors that are involved in the onset of multiple types of epilepsy are affected by CBDV. This cannabinoid has shown anti-seizure effects in a range of studies.
In this 2018 study, CBDV lessened neurobehavioral symptoms found in Rett Syndrome, which is caused by an X chromosome mutation. A study in 2019 showed that CBDV was able to correct memory deficits in mice with the same X chromosome defect.
CBDV has shown promise for treating the terrible effects of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. This debilitating disease is known to cause irreversible muscle damage and degeneration. Patients also experience chronic inflammation. In addition to reducing inflammation, CBDV can also restore some muscle function.
In this double-blind, placebo controlled study, CBDV was studied for its effects on autism in individuals aged 5-18. Research is on-going, but this cannabinoid shows promise for cognitive and communication related challenges as well as behavioral issues.

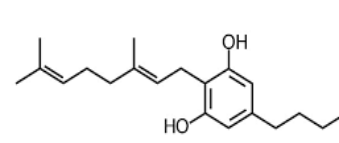
CBG
Cannabigerol (CBG) is the chemical precursor to several other major cannabinoids, including CBD and THC. The conversion to these cannabinoids usually takes place between weeks 6 and 8 of flower. CBG was found only in trace amounts in most strains, but more recently, growers have selectively bred strains high in CBG.
CBG interacts with CB1 and CB2 receptors. It likely inhibits the psychoactive effects of THC and may also block serotonin receptors and GABA intake. By inhibiting these, it may be beneficial as an antidepressant and anti-anxiety treatment.
Some of the other therapeutic benefits that CBG has been studied for include lowering intraocular pressure often found in Glaucoma, acting as an antibacterial and antifungal agent, reducing inflammation, antioxidant properties, and acting as a neuroprotectant.

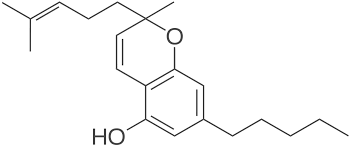
CBC
Cannabichromene (CBC) is a non-pyschoactive cannabinoid. While it does not bind well to CB1 receptors, it binds well to the vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) and the transient receptor potential ankyrin 1(TRPA1). When CBC binds to these receptors, it causes the body to release increased levels of the natural endocannabinoid, anandamide, which is related to pain perception. Pain relief is only one of the many benefits of CBC. Research has shown that CBC can reduce inflammation, regulate gastrointestinal motility, and act as a neuroprotectant.

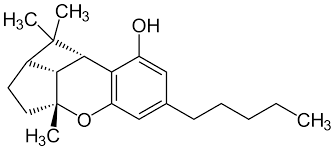
CBL
Cannabicyclol (CBL) is a non-psychoactive cannabinoid produced when CBC breaks down over time. It occurs in very minimal amounts in cannabis trichomes and is difficult to extract. Because of this, it has not been studied as often as the other cannabinoids. The research that has been done shows that CBC has anti-inflammatory properties, can relieve pain, and may have neuroprotective properties.

CBN
Cannabinol (CBN) is found only in trace amounts in hemp flower, but as THCA is heated or degrades over time, it can turn into CBN. It has been shown to be a powerful sedative, but is not known to be psychoactive. CBN has been shown to delay symptom onset of Lou Gehrig’s disease in mice. It also has anti-inflammatory and pain relieving properties.

Δ9 THC
Δ9 THC is a cannabinoid widely known for its psychoactive effects. It begins as THCA, tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, and converts to THC through a process called decarboxylation. Heating THCA causes it to release a carboxyl group and become Δ9 THC. Only after conversion is it able to bind to CB receptors.
Though most widely known for its psychoactive effect, the “high” that is associated with cannabis, Δ9 THC has been studied for many therapeutic benefits. It has been shown to reduce nausea, relieve pain and inflammation, help with digestive issues, and increase appetite. It also has anti-tumor properties. Hemp products containing a very minute amount (<0.30%) of Δ9 THC have not been shown to cause any psychoactive effects.

THCV
Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is similar in structure to Δ9 THC, but has very different effects. It has not been shown to be psychoactive and has been studied for numerous potential benefits. THCV is a powerful appetite suppressant and may aid in weight loss. It has been used to stimulate bone growth and is therefore being looked at as a treatment for Osteoporosis. Like CBDV, it has been shown to reduce seizures.
All of our hemp plant extract tinctures are high in CBD, CBC, CBG, and CBDV